OUR ADVANCED BREAST RADIATION PROGRAMS
Organ Sparing Radiotherapy Technique (VMAT)
The Problem
For breast cancer patients who require regional nodal irradiation, this involves including additional lymph node drainage areas in the radiation field such as the supra-clavicular region, the internal mammary nodal region and the axillary region.
Using conventional radiotherapy to treat all these areas results in a much greater amount of normal tissue (heart and lungs) being irradiated. This is because conventional radiotherapy is unable to conform tightly to these areas and more adjacent normal tissues are within the radiation field.
Technological Solution
Volumetric Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Complex Regional Nodal Irradiation
With VMAT, the radiation beams are delivered by arcs as the radiotherapy machine rotates around the patient. This effectively reduces the dose to the heart and lungs without compromising on the coverage of the targeted areas. VMAT can deliver a more conformal treatment compared to conventional radiotherapy and a faster treatment time as well.
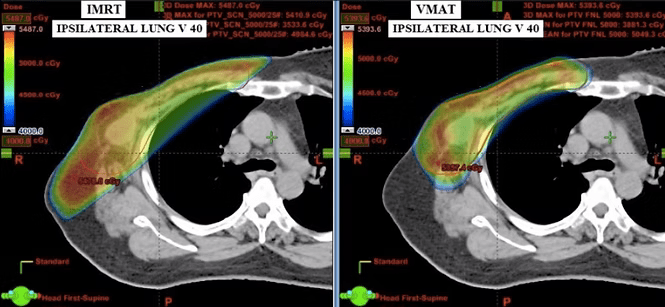
Chest wall plan comparison: IMRT vs VMAT, axial planning CT image with dose in colour wash showing ipsilateral lung V40 (volume of lung receiving minimum dose of 40 Gy).